Components of a PC System ( vocabulary ) ( exercises)

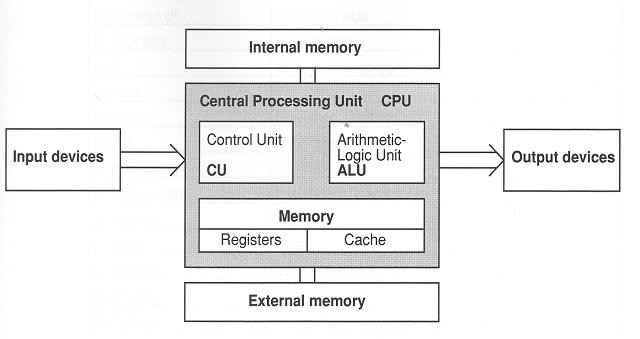
A PC system consists of the CPU (Central Processing Unit) and its peripheral devices like input and output devices, and internal and external memory.
The CPU, also called microprocessor, mainly contains
- an ALU (Arithmetic-Logic Unit) for manipulating data,
- a CU (Control Unit) for fetching and executing instructions,
- registers for holding temporary results of calculations and system state
information,
- a cache memory for holding instructions and data that are likety to be needed
next.
The internal memory, called main memory or RAM (Random-Access Memory),
temporarily stores any program executed by the computer and the data on which
the program operates.
Internal memories consist of chips that are designed für high-speed access
to information.
The external memory, called secondary memory or external storage, permanently
stores system programs and applications software. Information is transferred
to internal
memory when needed.
External memory devices, like magnetic or optical drives, may be internal or
external devices (built in the system unit or not).
I/O (Input/Output) hardware allows the user to interact directly with the
computer.
input hardware includes keyboards, scanners, digital cameras, microphones,
etc.
Output hardware includes monitors, printers, loudspeakers, etc.
All peripheral components are connected to the CPU via internal bus systems or external interfaces like serial and parallel ports, USB (Universal Serial Bus), and FireWire.